Calculating Acceleration (GCSE Physics)
Calculating Acceleration
Calculating Acceleration
For distance-time graphs, the gradient is the speed.
Table of Contents
For velocity-time graphs, the gradient is the acceleration.
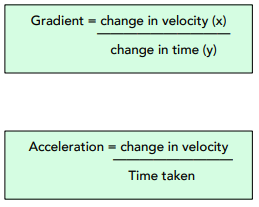
The question below shows how we can calculate acceleration from a velocity-time graph. If you are unsure why the gradient of the velocity time graph tells us the acceleration, then consider the two equations below:
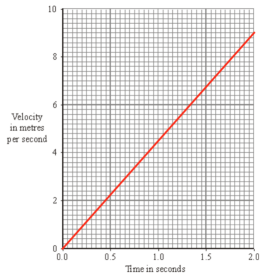
Question: (Following on from the previous question in the last tutorial). Calculate the acceleration of the athlete, using the graph you have just drawn.
1. Acceleration is the gradient.
From the graph, we need to find the gradient in order to know the acceleration.
2. Find the time and velocity.
From the graph, we can work out the values for time and velocity.
Time = 2 seconds
Velocity = 9 m/s
3. Use the gradient equation.
Now that we have values for distance and time, we can use our formula change in y / change in x to find the acceleration.
Gradient = change in y / change in x
Gradient = 9 / 2
Gradient = 4.5
Gradient = acceleration
Acceleration = 4.5 m/s²








Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment